M1 MABS Graphes TP Parcours en largeur - Plus court chemin
From silico.biotoul.fr
(Difference between revisions)
m (→Plus court chemin - Bellman-Ford) |
m (→Parcours en largeur) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
BFS(G, s) | BFS(G, s) | ||
'''for each''' vertex u <math>\in</math> V(G) | '''for each''' vertex u <math>\in</math> V(G) | ||
| - | '''do''' color[u] <math>\leftarrow</math> | + | '''do''' color[u] <math>\leftarrow</math> WHITE |
| - | d[u] <math>\leftarrow</math> | + | d[u] <math>\leftarrow</math> <math>\infty</math> |
| - | + | <math>\pi</math>[u] <math>\leftarrow</math> NIL | |
| - | color[s] <math>\leftarrow</math> | + | color[s] <math>\leftarrow</math> GRAY |
d[s] <math>\leftarrow</math> 0 | d[s] <math>\leftarrow</math> 0 | ||
Q <math>\leftarrow</math> <math>\empty</math> | Q <math>\leftarrow</math> <math>\empty</math> | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
'''while''' Q <math>\ne</math> <math>\empty</math> | '''while''' Q <math>\ne</math> <math>\empty</math> | ||
'''do''' u <math>\leftarrow</math> dequeue(Q) | '''do''' u <math>\leftarrow</math> dequeue(Q) | ||
| - | '''for each''' v <math>\in</math> Adj[u] | + | '''for each''' vertex v <math>\in</math> Adj[u] |
| - | '''do if''' color[v] = | + | '''do if''' color[v] = WHITE |
| - | '''then''' color[v] <math>\leftarrow</math> | + | '''then''' color[v] <math>\leftarrow</math> GRAY |
d[v] <math>\leftarrow</math> d[u] + 1 | d[v] <math>\leftarrow</math> d[u] + 1 | ||
| - | + | <math>\pi</math>[v] <math>\leftarrow</math> u | |
enqueue(Q, v) | enqueue(Q, v) | ||
| - | color[u] <math>\leftarrow</math> | + | color[u] <math>\leftarrow</math> BLACK |
'''Charger''' le graphe de la séance précédente ([[File:M1MABS Graphe dressing.sif]]), et effectuer un parcours en largeur depuis sous-vetements. | '''Charger''' le graphe de la séance précédente ([[File:M1MABS Graphe dressing.sif]]), et effectuer un parcours en largeur depuis sous-vetements. | ||
Revision as of 15:36, 19 February 2015
Contents |
Parcours en largeur
Algorithme :
BFS(G, s) for each vertex uV(G) do color[u]
WHITE d[u]
π[u]
NIL color[s]
GRAY d[s]
0 Q
enqueue(Q, s) while Q
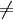
do u
dequeue(Q) for each vertex v
Adj[u] do if color[v] = WHITE then color[v]
GRAY d[v]
d[u] + 1 π[v]
u enqueue(Q, v) color[u]
BLACK
Charger le graphe de la séance précédente (File:M1MABS Graphe dressing.sif), et effectuer un parcours en largeur depuis sous-vetements.
Plus court chemin - Bellman-Ford
Rappel de l'algorithme:
INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, s) for each vertex vV(G) do d[v]
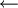
π[v]
NIL d[s]
0 RELAX(u, v, w) if d[v] > d[u] + w(u, v) then d[v] = d[u] + w(u,v) π[v]
u BELLMAN-FORD(G, w, s) INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, s) for i
1 to |V(G)| - 1 do for each edge (u,v)
E(G) do RELAX(u, v, w)
Plus courts chemins - Floyd-Warshall
Pour l'agorithme suivant,
- D[x,y] est la distance du plus court chemin entre les sommets x et y
- N[x,y] est le successeur de x dans le plus court chemin allant de x à y
- W[x,y] est la valuation de l'arc (x,y)
Algorithme :
initialiser D = W, et N
pour k de 1 à n
pour i de 1 à n
pour j de 1 à n
si D[i,k] + D[k,j] < D[i,j] alors
D[i,j] = D[i,k] + D[k,j]
N[i,j] = k
Récupération du plus court chemin à partir de la matrice N :
plusCourtChemin(D,N, i,j)
si D[i,j] est infinie alors
il n'y a pas de chemin entre i et j
chemin = initialiserChemin(i)
k = N[i,j]
tant que k est défini faire
ajouter(chemin, k)
k = N[k,j]
ajouter(chemin, j)
Implémenter les algorithmes ci-dessus en R et les tester sur la matrice suivante :
# adjacency matrix M=matrix( c(0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0), ncol=4, byrow=T) M # [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] #[1,] 0 1 0 0 #[2,] 1 0 0 1 #[3,] 0 0 1 1 #[4,] 0 0 0 0 # test fw=FloydWarshall(M) fw #$distances # [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] #[1,] 2 1 Inf 2 #[2,] 1 2 Inf 1 #[3,] Inf Inf 1 1 #[4,] Inf Inf Inf Inf # #$chemins # [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] #[1,] 2 NA Inf 2 #[2,] NA 1 Inf NA #[3,] Inf Inf NA NA #[4,] Inf Inf Inf Inf FloydWarshallPath(fw, 1,4) #[1] 1 2 4
Extraire la grosse composante connexe de String au format sif puis transformer le fichier en matrice d'adjacence. Ensuite, sous R, charger la matrice et calculer le diamètre du graphe.